Have you ever wondered how search engines know exactly what your web content is about and display it in a way that stands out on the results page? The secret often lies in schema markup.
Schema markup is a form of structured data that helps search engines understand the content of your website more effectively.
By adding schema markup to your web pages, you can enhance your content’s visibility, improve user experience, and even increase click-through rates (CTR).
In this article, we’ll dive into what schema markup is, how it works, why it’s crucial for SEO, and how you can use it to boost your website’s performance.
What is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is a form of structured data, or code, that helps search engines interpret the content of your website in a way that’s more organized and detailed. It’s a language of tags that you add to your website’s HTML code to provide context about the content.
Essentially, schema markup tells search engines what a specific piece of content means, rather than just what it says.
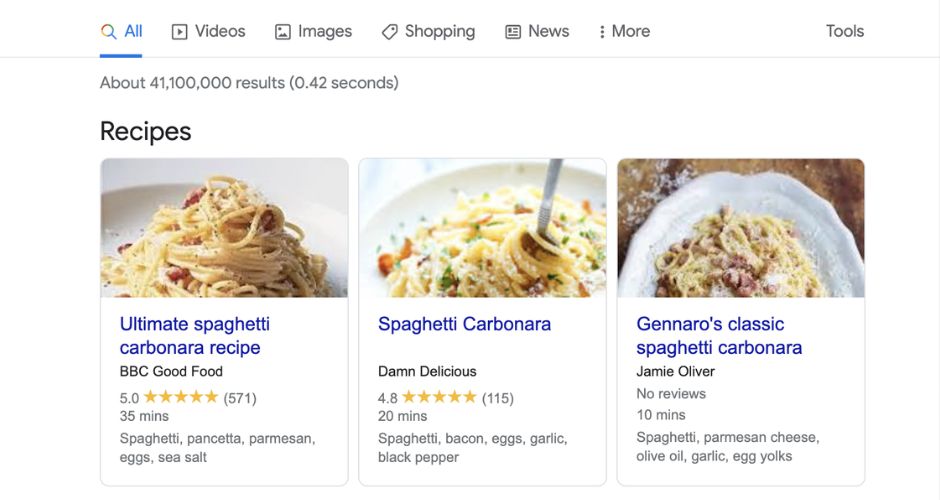
For example, if you have a recipe on your website, schema markup can specify details such as cooking time, ingredients, ratings, and nutritional information. This extra data helps search engines like Google deliver more relevant, informative search results to users.
The Origins of Schema Markup
Schema markup was developed by schema.org, a collaborative effort from major search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex. The goal was to create a standardized vocabulary of tags that website owners and developers could use to label their content, making it easier for search engines to interpret. As of today, schema markup is supported by nearly all search engines, making it a critical tool for SEO.
How Schema Markup Works
Structured data is a standardized format used to define information about a web page. In the case of schema markup, this data helps search engines understand the relationships between various elements on a page.
This means that instead of simply looking at keywords and links, search engines can better understand the actual content of a page, such as whether it’s an article, a product listing, or a local business.
For example, when a recipe website adds schema markup, the search engine can identify the name of the dish, ingredients, cooking time, and other key pieces of information. This data is then used to enhance the search result snippets that users see in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Types of Schema Markup
There are three primary types of schema markup: JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa. Let’s briefly look at each:
- JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data): This is the most commonly used format. It’s easy to implement and does not affect the visible content of the page.
- Microdata: This type involves embedding structured data within the HTML code of a page.
- RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes): Similar to Microdata but typically used for more complex data types.
For most websites, JSON-LD is recommended due to its simplicity and flexibility.
How Schema Markup is Implemented
Schema markup can be implemented manually by editing the HTML code of a page or automatically through plugins. For instance, if you’re using WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO or Schema Pro can simplify the process. Here’s how you might implement schema markup:
- Manual Implementation: Add the appropriate schema tags directly into your website’s HTML.
- Using Plugins: Use a plugin to generate and implement the code automatically.
There are also tools available to help generate schema code, such as Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper.
Importance of Schema Markup for SEO
Improved Click-Through Rates (CTR)
One of the most immediate benefits of schema markup is the potential to increase your website’s click-through rates (CTR). When your content is marked up with schema, search engines can display rich snippets-enhanced search results that provide users with more detailed information. For instance, an article with schema markup may appear with star ratings, review counts, or the publication date, making it more appealing to users.
Example: A restaurant review page might show up in search results with a star rating and price range. This information helps users quickly assess whether they want to click on your link.
Enhanced Rich Snippets
Schema markup enables rich snippets, which are enriched search results that provide more information than the typical blue link. These snippets often include ratings, product prices, business hours, and other useful data.
For instance, a recipe schema can display preparation time, ingredients, and even user reviews directly in search results, encouraging more clicks.
Example: A recipe page may appear in search results with the following rich snippet:
- “Prep Time: 15 minutes”
- “Cook Time: 30 minutes”
- “Rating: 4.5 stars based on 200 reviews”
Better Ranking Opportunities
Schema markup can also help improve your rankings. While schema itself is not a direct ranking factor, it does contribute to search engines better understanding and categorizing your content, which can lead to higher rankings.
Additionally, schema markup can help your content appear in featured snippets (position 0), which is prime real estate in SERPs.
Example: A page marked with FAQ schema may appear in a box at the top of the search results, directly answering a user’s question.
Local SEO Benefits
For businesses that rely on local traffic, schema markup is essential. LocalBusiness schema allows search engines to display your business address, phone number, hours of operation, and even customer reviews. This increases the likelihood of your business appearing in local searches, making it easier for customers to find you.
Example: A local coffee shop can add schema markup to show their location, business hours, and reviews directly in search results, making it more accessible to people searching for “coffee near me.”
Common Types of Schema Markup
Article Schema
This schema is ideal for blogs, news articles, and other forms of content. It helps search engines recognize your content as an article and display it with relevant details, such as the author, publication date, and images.
Example: An article on “10 Best SEO Tips for 2024” can display the author’s name, publication date, and a featured image directly in the search results.
Product Schema
E-commerce sites can benefit greatly from product schema. This type of schema includes details such as pricing, availability, and product ratings, which are then shown in the search results.
Example: A product listing for a smartphone can display the price, user ratings, and availability status directly in search results.

Organization Schema
This schema is used to mark up business details like name, logo, contact information, and social media profiles. It ensures that your business appears correctly in search results and is connected to your online presence.
Example: An organization schema for a digital marketing agency can display the company name, logo, and contact information.
FAQ Schema
The FAQ schema is used to mark up frequently asked questions on your site, allowing search engines to display questions and answers directly in the search results.
Example: A page answering “What is Schema Markup?” could display the question and a concise answer directly in the SERP.
Event Schema
Event schema is essential for businesses that host or promote events. It includes event details such as time, location, ticket price, and availability.
Example: A concert listing page can use event schema to display the event date, venue, and ticket information directly in the search results.
Benefits of Schema Markup for SEO
- Improved Content Discovery: By providing structured data, schema markup helps search engines better understand the content of your page, leading to better content visibility.
- Increased Website Traffic: The rich snippets created by schema markup attract more users to your website by providing them with useful, visible information directly in search results.
- Enhanced User Experience: Schema markup enriches how users interact with your content in search results, increasing trust and satisfaction.
How to Implement Schema Markup
Step-by-Step Guide for Adding Schema Markup
- Use the Google Structured Data Markup Helper to create and implement schema.
- Manually add the schema code to your website’s HTML or use CMS plugins like Yoast SEO or Schema Pro.
- Once implemented, use the Google Structured Data Testing Tool to ensure there are no errors.
Testing Schema Markup
After adding schema markup, use tools like Google Search Console and Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to validate your structured data and ensure everything is working correctly.
Challenges of Schema Markup
- Complexity and Errors: Implementing schema markup can be challenging for beginners, and mistakes can lead to errors in search engine displays.
- Algorithm Changes: Search engines regularly update their algorithms, which can affect how schema data is used in rankings and rich snippets.
Future of Schema Markup in SEO
- Schema’s Role in Featured Snippets: As search engines evolve, schema markup will continue to play an important role in positioning content in featured snippets and other premium search result areas.
- Impact on Voice Search and AI: With the rise of AI and voice search, structured data will become even more critical for helping search engines deliver accurate, context-rich answers.
Conclusion
Schema markup is no longer optional for SEO-it’s an essential tool that helps search engines better understand your website’s content, making it easier for users to find and interact with it.
By adding schema to your web pages, you can improve click-through rates, rank better in search results, and enhance your website’s visibility. If you haven’t already, it’s time to start implementing schema markup to take your SEO strategy to the next level.
FAQs
- What is the difference between schema markup and structured data?
Schema markup is a form of structured data that follows the guidelines provided by schema.org to help search engines understand content. - Can schema markup improve my website’s ranking?
While schema itself isn’t a ranking factor, it helps search engines understand and categorize your content better, leading to potential ranking improvements. - Is schema markup a ranking factor for Google?
Schema markup isn’t a direct ranking factor, but it improves content visibility, which can influence ranking indirectly. - Can I use multiple types of schema markup on a single page?
Yes, you can implement multiple types of schema markup on a page as long as they are relevant to the content. - How can I check if schema markup is working on my website?
Use tools like the Google Structured Data Testing Tool or Google Search Console to test and validate your schema implementation.


