Google’s search algorithm is constantly evolving to provide users with the most relevant, high-quality results. Core updates are major algorithm changes that can significantly impact website rankings. Understanding these updates helps website owners, marketers, and SEO professionals adapt their strategies and maintain strong visibility.
This guide covers the most important Google core updates from 2011 through 2025, explaining their purpose, effects, and real-world examples.
What Are Google Core Algorithm Updates?
Google’s core algorithm updates are significant changes to the way the search engine evaluates and ranks websites. Unlike minor tweaks, these updates can cause noticeable shifts in search rankings, rewarding sites that follow best practices and penalizing those that rely on outdated SEO tactics or low-quality content.
Google releases core updates periodically to improve search results by:
- Enhancing content quality evaluation
- Improving user experience signals
- Reducing spam and manipulative practices
- Recognizing expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-A-T)
Below is a detailed breakdown of every significant update, their impact, examples, and direct links to trusted sources for deeper reading.
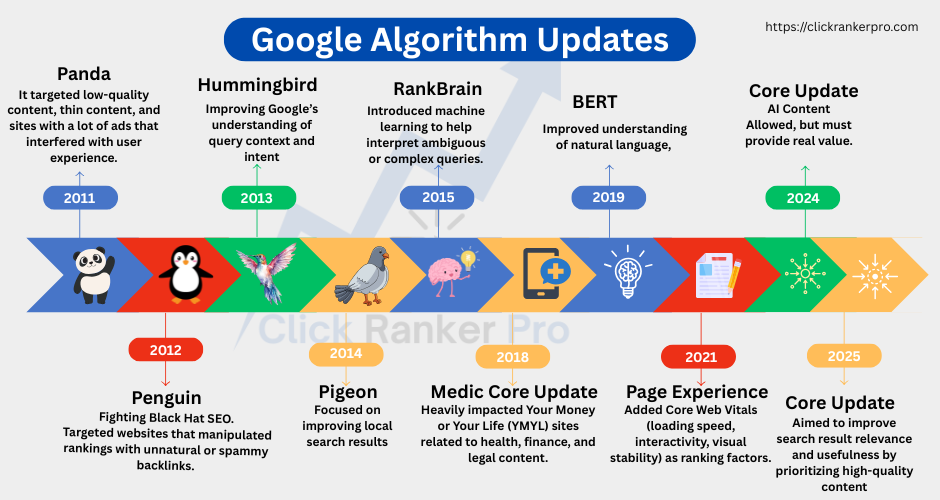
1. Panda Update (February 2011)
What: Panda targeted low-quality content, thin content, and sites with a lot of ads that interfered with user experience.
Why: Google wanted to reward websites that provided original, valuable, and well-written content while penalizing content farms and spammy sites.
Example:
- Before Panda: Demand Media’s eHow (a content farm with lots of low-value articles) ranked very high.
- After Panda: eHow’s traffic dropped significantly, encouraging them to improve content quality.
2. Penguin Update (April 2012)
Fighting Black Hat SEO
What: Penguin targeted websites that manipulated rankings with unnatural or spammy backlinks.
Why: To stop sites from using link schemes, buying links, or link farms that inflated their search rankings unfairly.
Example:
- A small business buying cheap backlinks from unrelated websites saw its ranking tanked after Penguin. After cleaning up its backlink profile, the site recovered.
3. Exact Match Domain (EMD) Update (September 2012)
What: This update penalized low-quality sites that ranked well solely because their domain exactly matched popular search terms.
Why: To improve search result quality by preventing poor sites with keyword-heavy domain names from ranking without good content.
Example:
- A site called best-cheap-laptops.com ranking on the first page despite shallow content saw a drop in ranking after the update.
4. Hummingbird Update (August 2013)
What: Hummingbird was a major overhaul improving Google’s understanding of query context and intent, especially for conversational and long-tail searches.
Why: To move beyond simple keyword matching and focus on meaning behind queries.
Example:
- Before Hummingbird: Searching “best place to eat near me” might return results for “best place to eat” globally.
- After Hummingbird: Google understands “near me” and localizes results based on user location.
5. Pigeon Update (July 2014)
What: Focused on improving local search results by tying them more closely to traditional web ranking signals.
Why: To provide more accurate and relevant local business listings.
Example:
- A restaurant just outside city limits that previously wasn’t visible now appeared for local searches within the city due to better local SEO integration.
6. Mobile-Friendly Update (“Mobilegeddon”) (April 2015)
What: Boosted mobile-friendly websites in mobile search results.
Why: As mobile traffic surged, Google wanted to reward sites optimized for mobile users.
Example:
- An e-commerce site without a mobile version lost significant mobile search traffic, while a competitor with a responsive site rose in rankings.
7. RankBrain Update (October 2015)
What: Introduced machine learning to help interpret ambiguous or complex queries.
Why: To better understand the user’s intent and deliver more relevant results for long-tail or unusual searches.
Example:
- For the query “Can you get medicine for someone else?”, RankBrain helps Google grasp the context and show appropriate results.
8. Possum Update (September 2016)
What: Tweaked local search results to diversify listings and filter out duplicate or spammy businesses.
Why: To increase variety in local search results and ensure businesses near the searcher get visibility.
Example:
- Businesses located just outside city boundaries began appearing in local search packs for users inside the city.
9. Fred Update (March 2017)
What: Targeted sites focused heavily on ad revenue with low-quality content.
Why: To penalize websites that prioritized monetization over providing valuable content.
Example:
- Affiliate marketing blogs stuffed with ads and minimal useful content saw sharp traffic declines.
10. Medic Core Update (August 2018)
What: Heavily impacted Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) sites related to health, finance, and legal content.
Why: Google emphasized E-A-T (Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness) for sites that affect user wellbeing.
Example:
- A non-expert medical advice blog dropped in rankings, while established health portals like WebMD and Mayo Clinic improved.
11. BERT Update (October 2019)
What: Improved understanding of natural language, focusing on prepositions and nuances in queries.
Why: To better interpret the context and intent of conversational queries.
Example:
- Queries like “2019 brazil traveler to usa need a visa” returned better-targeted results, understanding the exact meaning rather than keyword matching.
12. May 2020 Core Update
What: Broad update focused on rewarding comprehensive, user-focused content.
Why: Google continued improving how it measures quality and relevance.
Example:
- Many sites with shallow content experienced ranking fluctuations; sites with detailed and authoritative content benefited.
13. December 2020 Core Update
What: Further refined content quality and user experience signals.
Why: To push sites with richer, trustworthy content higher in rankings.
Example:
- Websites with thorough resources and clear expertise saw ranking gains.
14. Page Experience Update (June 2021)
What: Added Core Web Vitals (loading speed, interactivity, visual stability) as ranking factors.
Why: To enhance user experience by rewarding faster, smoother websites.
Example:
- Websites with slow load times or annoying pop-ups lost rankings to faster, well-optimized competitors.
15. Product Reviews Update (July 2021)
What: Rewarded in-depth, authentic product reviews over thin or generic ones.
Why: To help users find reviews with real insights rather than superficial summaries.
Example:
- Blogs with detailed product testing and personal experience outranked sites with generic reviews.
16. Link Spam Update (November 2021)
What: Improved detection and demotion of sites using manipulative link schemes.
Why: To ensure link-building remains natural and trustworthy.
Example:
- Sites buying large numbers of low-quality backlinks saw ranking drops.
17. December 2021 Core Update
What: Continued emphasis on content quality and relevance.
Example:
- Sites providing clear, well-structured content continued to see growth.
18. June 2022 Core Update
What: Focused on rewarding fresh, relevant content.
Example:
- News and informational sites that updated frequently saw improved rankings.
19. August 2022 Core Update
What: Reinforced importance of topical authority and content depth.
20. March 2024 Core Update
What: Integrated Helpful Content signals directly into core ranking.
Why: To penalize content created mainly for SEO rather than user benefit.
21. August 2024 Core Update
What: Further rewarded original, in-depth content over keyword-stuffed or copied pages.
March 2025 Core Update (March 13–27, 2025)
Goal:
Improve the usefulness, relevance, and authenticity of content in Google Search by reducing visibility of low-quality or SEO-first pages and promoting truly helpful content written with real expertise and user value in mind.
Key Focus Areas of the Update:
- Deindexing “unhelpful” content: Pages made primarily for search rankings rather than humans were removed from results.
- Site-wide impact: A few poor-quality pages could bring down the entire domain’s performance.
- Hidden helpful content system: Integrated signals from the Helpful Content System directly into Google’s core ranking system.
- Reduced reliance on AI-spun content: Content clearly written for rankings or made using low-effort AI tools was penalized.
- Shift toward topical authority: Niche experts and authentic voices gained visibility.
🟥 Loser Example: Affiliate SEO Blog
- Before Update:
A generic blog, bestproductreviews247.com, was ranking on Page 1 for product reviews by using:
- Mass-produced AI content
- Keyword stuffing like “best wireless headphones under $100”
- Dozens of affiliate links
- Little original insight or product use experience
- Mass-produced AI content
- After Update (March 2025):
The site saw a 70–90% drop in organic traffic. Google identified it as:
- Created primarily for monetization
- Lacking authentic value
- Not authored by credible experts
- Created primarily for monetization
✅ Winner Example: Real Expert Website
- Before Update:
TheAudioNerd.com, a smaller site run by a professional audio engineer, had:
- Fewer backlinks
- Slower growth
- Detailed reviews based on real-world testing
- Photos, audio samples, and user-centric insights
- Fewer backlinks
- After Update:
Rankings skyrocketed for terms like “best wireless headphones for mixing” and “audio interface comparison 2025” because:
- The content demonstrated expertise, first hand experience, and trustworthiness
- Google now prioritized content quality over SEO tactics
- The content demonstrated expertise, first hand experience, and trustworthiness
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How often does Google release core updates?
Google typically releases broad core updates several times a year, alongside smaller, targeted updates.
Q2: How can I recover from a core update penalty?
Focus on improving content quality, user experience, expertise, and authoritative backlinks. Avoid quick fixes or spammy tactics.
Q3: What is E-A-T, and why does it matter?
E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. It’s a key quality guideline Google uses to assess the credibility of content, especially in sensitive topics.
Q4: Should I change my entire SEO strategy after a core update?
Not necessarily. Analyze the affected pages, identify gaps in quality or relevance, and make targeted improvements.
Q5: How do I stay updated on Google’s algorithm changes?
Follow Google’s official Search Central blog, trusted SEO news sites, and industry experts.


